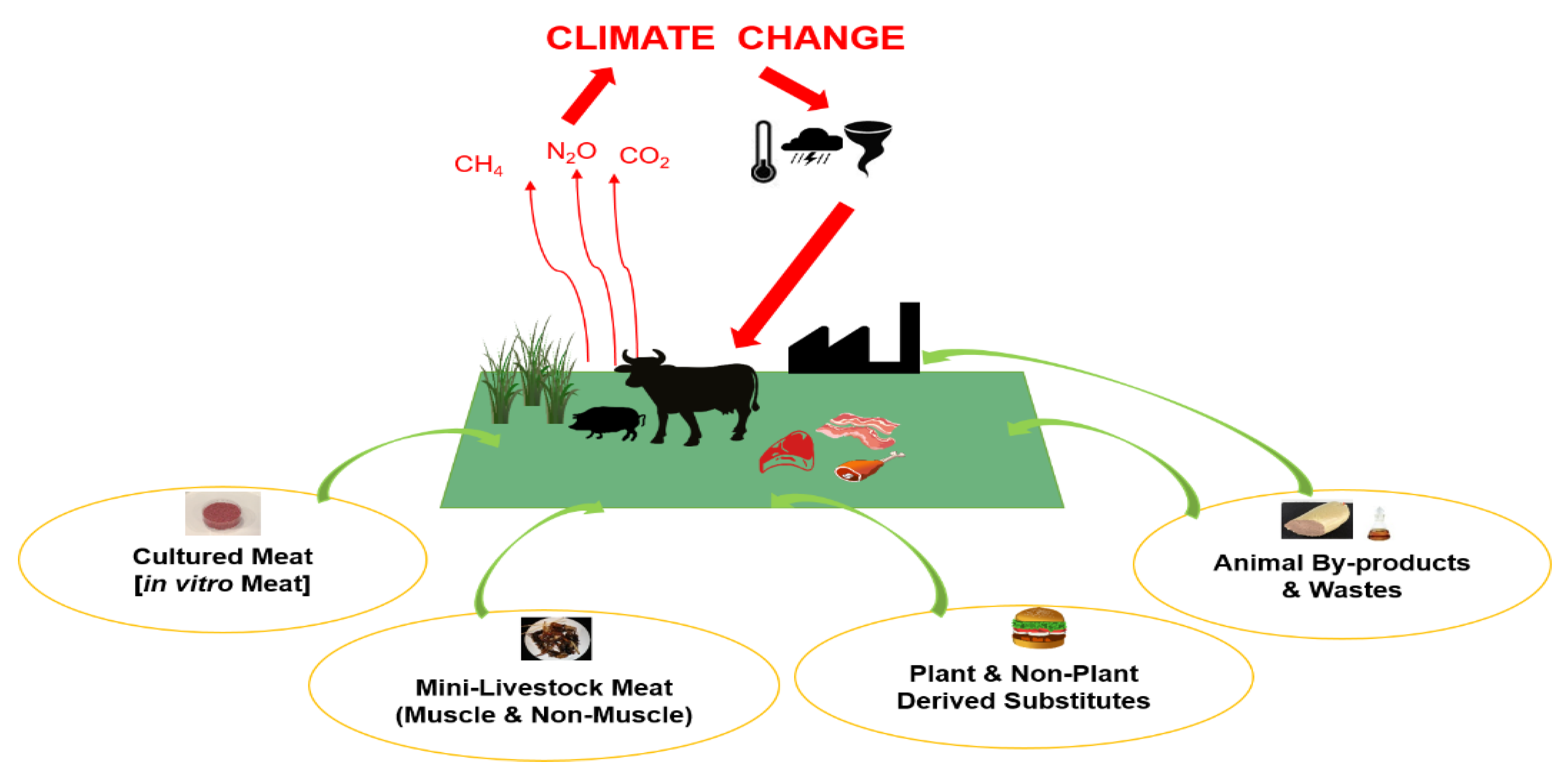
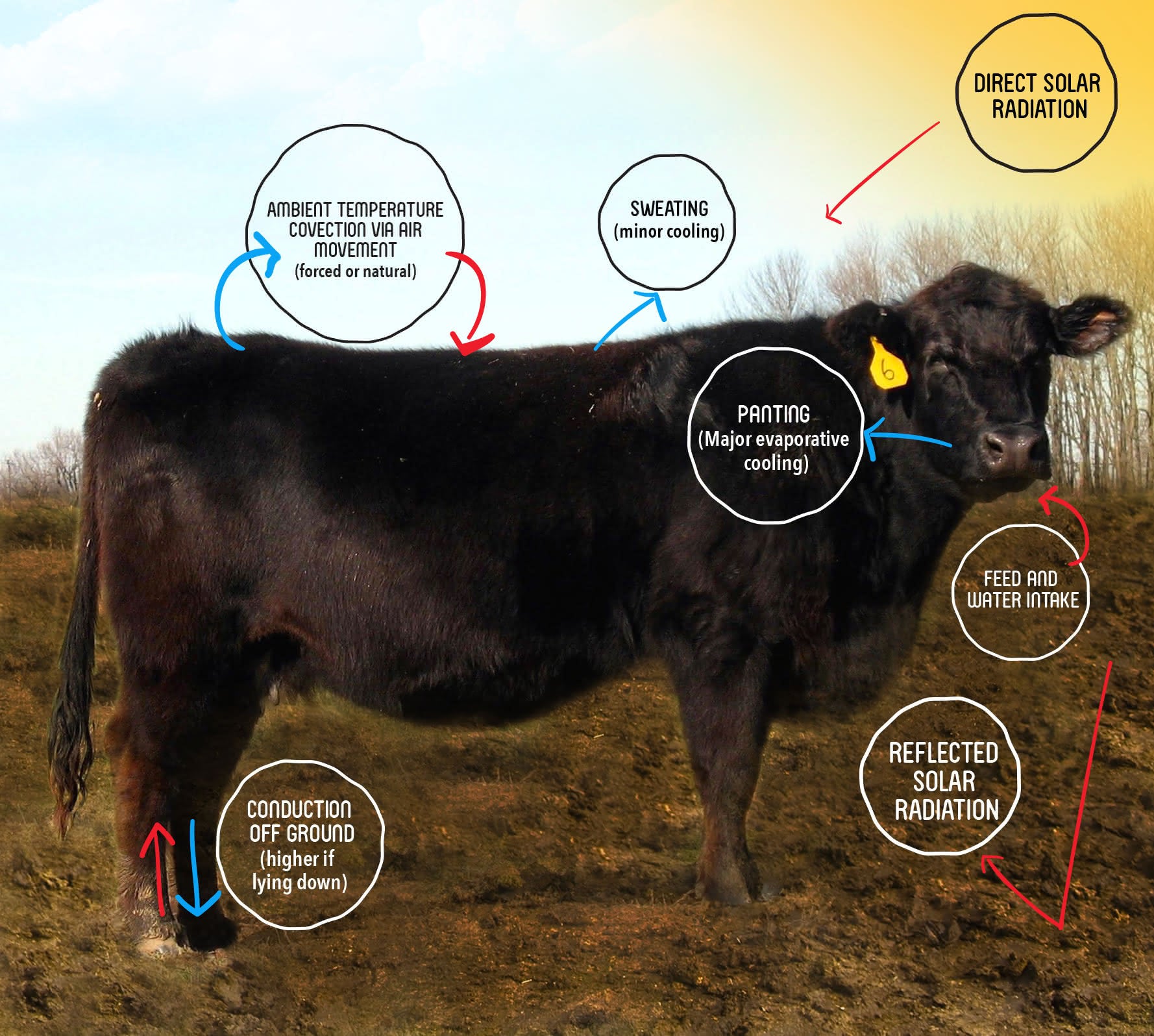
Cool Treatment Of Livestock In Balance Sheet
For depreciation Accumulated depreciation opening balance Depreciation for the year - Accumulated depreciation of disposed asset.
Treatment of livestock in balance sheet. Provisions are listed on a companys balance sheet. To get higher than 55 requires a higher level of management and would normally require rotating livestock twice or more per week. For committed lines of credit it makes sense to set the exposure at 100 of the commitment since the bank.
Basel 2 focuses on expected usage and EAD. The waste mixture is sent to the anaerobic biological digesters for treatment resulting in the extraction of biogas and a digestate from which a liquid fraction is separated 88 and a solid one 2. In other words provision is a liability of uncertain timing and amount.
The regulatory Basel 1 treatment of off balance sheet exposures is to use a CCF of 50 factor. Increase Utilization rate just to make the livestock needs and forage availability balance. Off balance sheet exposures can move up on balance sheet at any time.
As stated in Section 1231b3 to qualify as property used in trade or business livestock must be held by the taxpayer for draft breeding dairy or sporting purposes for at least twelve months twenty-four for cattle and horses. This approach works well for depreciable assets like machinery and buildings. They cannot be revalued.
In addition using proper feed manage-ment practices may improve net-farm income. Balance sheet value of the company. Below are beginning and ending balance sheets.
Change in Market Valuation. Machinery was valued at 709966 on the ending balance sheet. Self-Employment Tax 335 268 b Total Deferred Tax Liability Related to Base Value Treatment of Raised Breeding Livestock 4528 3622 Non-Current Portion of Deferred Taxes Related to Valuation Equity 19X2 19X1 Tax Basis Tax Basis Market Value Base Value Difference Market Value Base Value Difference Raised Breeding Livestock 10000 12500 2500 10000 10000 0 Purchased Breeding Livestock.